Choosing the right relay requires considering multiple factors to ensure it operates normally and reliably in a specific application. Below is a detailed explanation of each factor to help you better understand how to select the most suitable relay:
1.Contact Load
The contact load of a relay determines the maximum current, power, and voltage it can handle. It is essential to ensure the relay can withstand the current and voltage of the load, especially during startup, shutdown, or overload conditions. Inductive loads (such as motors or electromagnets) can generate arcs when switched, so it is important to select a relay with high arc resistance.
2.Contact Material
The contact material of a relay affects its lifespan and load compatibility. Common materials include:
1 Silver Alloy: Suitable for general resistive loads, offering good conductivity and wear resistance.
2 Gold Alloy: Ideal for low-current loads, especially where stable contact is needed in low current conditions.
3 Copper Alloy: Suitable for high-current loads, able to withstand higher currents and voltages, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. The choice of material should be based on the load type (inductive, resistive, or capacitive) and the operating environment.
3.Electrical Durability
Electrical durability refers to the number of reliable switch cycles the relay can perform under rated load conditions. High-frequency switching or inductive loads can accelerate wear on the relay, shortening its lifespan. It is essential to select a relay based on the switching frequency in your specific application to ensure its durability meets the required lifespan.
4.Voltage
The working voltage of the relay must match the voltage of the control circuit. Ensure the relay can operate reliably within its rated voltage range, as voltages that are too high or too low can cause malfunction. Some relays have wide voltage ranges and overvoltage protection features, which can accommodate environments with voltage fluctuations.
5.Coil Resistance
The coil resistance of a relay directly affects its power consumption. If the resistance is too high, a higher voltage may be needed to operate the relay; if too low, it could result in overheating. When selecting a relay, ensure the coil power consumption is compatible with the power supply’s voltage and current to avoid overheating or insufficient power.
6.Size and Mounting Clearance
The dimensions and mounting clearance of the relay are crucial, particularly in compact circuit boards or devices. Ensure that the relay’s physical size meets design requirements and that there is adequate space between the contacts and other components to prevent short circuits or other failures.
7.Other Considerations
1 Environmental Factors
The operating environment (such as temperature, humidity, and vibration) can affect the relay’s performance. In special environments, such as high temperatures, high humidity, or corrosive conditions, you may need to choose relays designed for higher environmental resistance, such as waterproof, dustproof, or corrosion-resistant models.
2 Reliability and Certification
Choose relays with recognized quality certifications (such as UL, CE, etc.) to ensure that they meet international standards for quality control and reliability. This is particularly important for applications where safety and reliability are critical.
Summary
When selecting a relay, it is essential to consider multiple factors, including load type, voltage, current, power consumption, and environmental conditions. Make sure the relay’s specifications and performance meet the actual requirements to ensure its stable and reliable operation in the intended application.
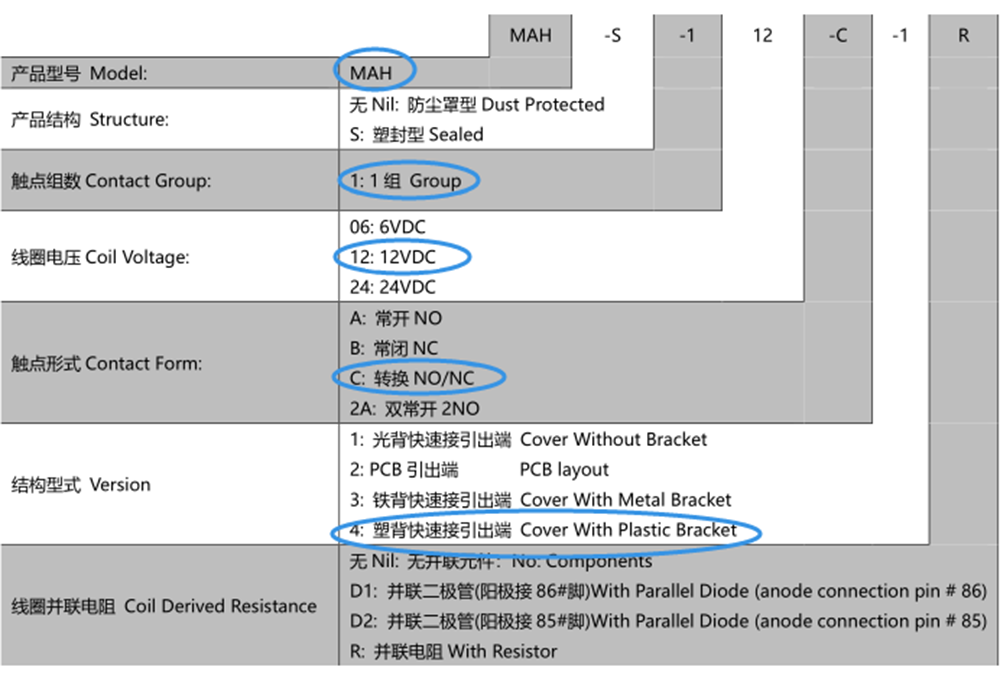
For example, our automotive relay: MAH-112-C-4, the selection is as follows: