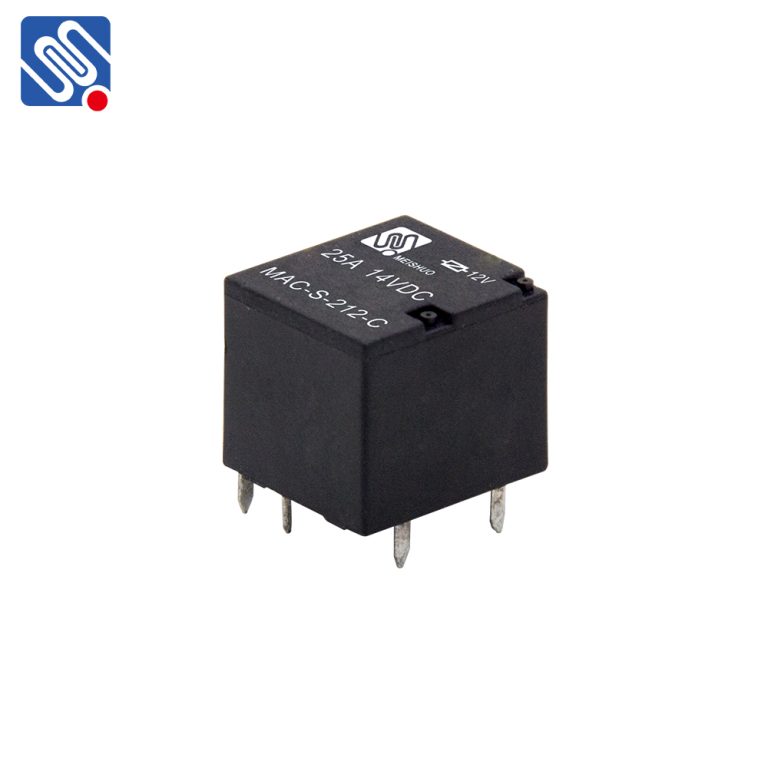
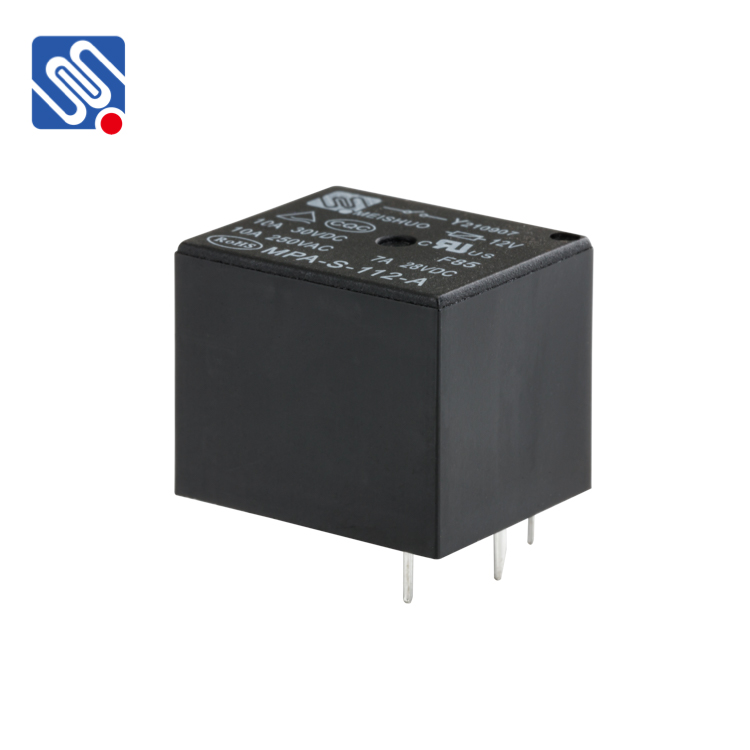
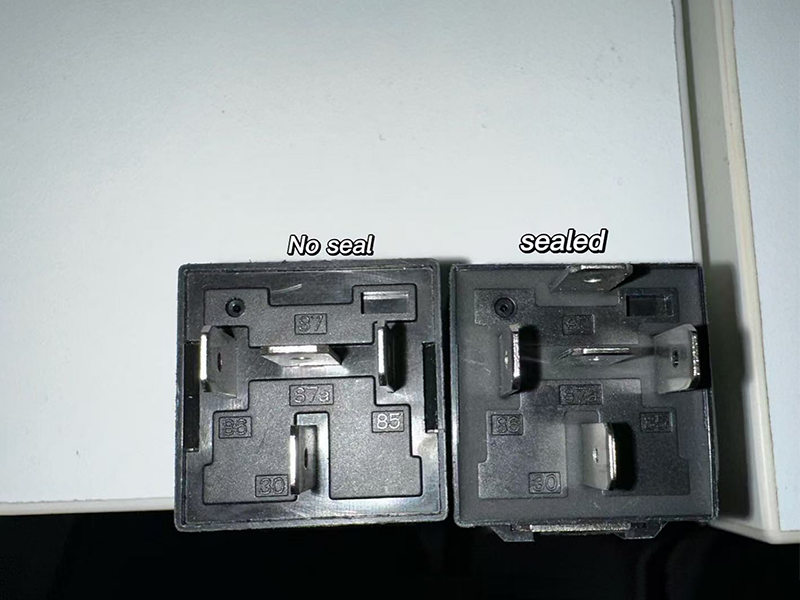
In recent years, with the widespread use of automation equipment and household appliances, relays have become essential electrical components in industries, home appliances, and automobiles. Among the different types of relays, sealed (plastic-sealed) and non-sealed relays are the most common. While both types of relays function in similar ways, they differ significantly in electrical durability. Research shows that sealed relays generally have higher electrical durability than non-sealed relays, particularly in applications involving frequent switching, high loads, or harsh environments.
Advantages of Sealed Relays
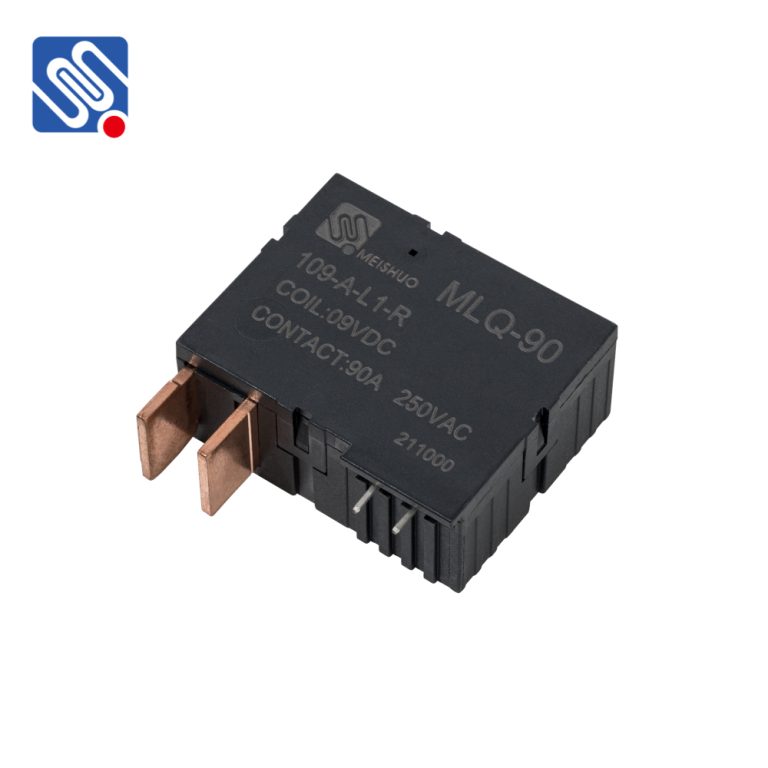
Sealed relays feature a closed design, with the relay’s electromagnetic coil and contact components encapsulated in a plastic or other insulating material, forming a completely sealed space that isolates the internal elements from external environmental factors. This encapsulation prevents dust, moisture, and corrosive gases from entering the relay, effectively reducing wear and corrosion of internal components. For equipment that requires long-term, frequent switching, sealed relays can significantly extend their service life and reduce failure rates.
During the switching process, particularly when dealing with higher loads, arcing is a common occurrence. Sealed relays reduce the exposure of the contacts to air, which helps suppress arcing, thereby minimizing contact wear and corrosion. This structure makes sealed relays more suitable for high-load, high-frequency switching applications.
Limitations of Non-Sealed Relays
In contrast, non-sealed relays have a simpler design, with no encapsulation to protect the internal components. The contacts and electromagnetic coil are exposed to the external environment, allowing dust, moisture, and corrosive gases to penetrate the relay. This exposure can lead to oxidation, corrosion, and wear of the contacts, resulting in lower electrical durability. Non-sealed relays are, therefore, less reliable, especially in high-load or high-humidity environments.
However, non-sealed relays do have certain advantages in specific applications. Due to their simpler design and lower cost, non-sealed relays are typically used in low-load, low-frequency switching scenarios, such as household appliances or basic control systems.
Practical Applications of Sealed Relays
In modern industrial control, automotive electronics, and home appliance products, sealed relays have become the preferred choice for high-demand applications due to their superior electrical durability. For example, in automated production lines, power control systems, and smart home devices, sealed relays can handle complex environments and frequent switching demands, ensuring the long-term stable operation of the equipment. In general, most standard relays used in household appliances and industrial control are sealed. The sealed design offers higher reliability and longer life expectancy, especially in environments where dust, moisture, or chemical exposure might be a concern. For automotive applications, relays are selected based on the specific environmental conditions. For instance, in situations where there is high humidity or the presence of harmful gases, automotive relays are more likely to use sealed designs to ensure better durability and prevent internal components from being damaged by these harsh conditions. This is especially important in automotive circuits, which may be exposed to water, salt, or exhaust gases, all of which can accelerate the degradation of non-sealed relays.
Conclusion
Overall, sealed relays typically offer higher electrical durability than non-sealed relays, especially in complex and harsh working environments. In fact, most general-purpose relays are sealed due to their higher reliability and longer lifespan. For automotive applications, where environmental factors such as humidity and corrosive gases play a major role, sealed relays are often the preferred choice. As technology continues to improve, sealed relays will continue to play a crucial role in applications requiring high-frequency, high-load switching. For equipment that needs to operate reliably over long periods, sealed relays are undoubtedly the better choice.
The picture shows our MAHjd1914 automotive relays. You can tell with your naked eye whether they are plastic sealed.